It’s a fact: people won’t use a website if they can’t find their way around it.
Looking for things in a website and looking for them in the real world have a lot of similarities. In many aspects of our life, we need signs of where we are and how we got there. We tend to search for sign guides while we browse, whether we are at the street, a supermarket or in a metro station.
There are many signs in a website showing where we are. In my Facebook profile page, I know where I am because I see my profile picture. In Amazon, I see a large picture of the product, so I know I’m in the product’s page.
Page title
Page titles are used in browser’s tabs, bookmarks, search engine result pages and by social media sites when linking to web pages. Some social media and social bookmarking web sites such as Digg and Facebook automatically retrieve the contents of the title tag when the user submits a URL.
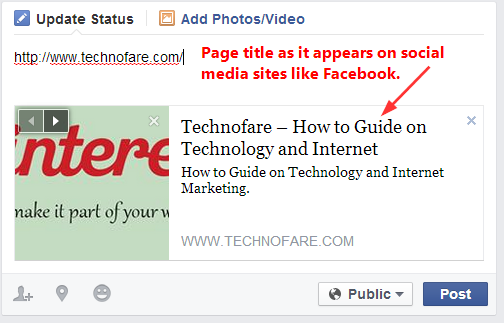
They are important for SEO but their main purpose is to communicate information about what the page is about. People can quickly figure out if they’re in the right place or not. A title may be fully optimized for search engine results, but it will be useless if a human cannot read and understand it also.
Logo
In a store, I only need to see the shop’s name on my way in, once I’m inside I know I’m still in the same shop until I leave. On the web things are kind of different though. The logo represents the whole site, which means it’s the highest item in the logical hierarchy. So the best place for it is at the top, where it conceptually frames the entire page. As a form of navigation the logo is expected to link to the homepage and is used as a reference point in every page. Users expect that, even if they get lost, by clicking at the logo they will go to homepage.
Breadcrumbs
A breadcrumb is a type of secondary navigation that reveals the user’s location in a website and can greatly enhance the way users find their way around. They are especially useful on sites that have some depth in the page hierarchy.
Breadcrumbs provide links back to each previous page the user navigated through to get to the current page or the parent pages of the current one.
Typical breadcrumbs look like this:

Tags
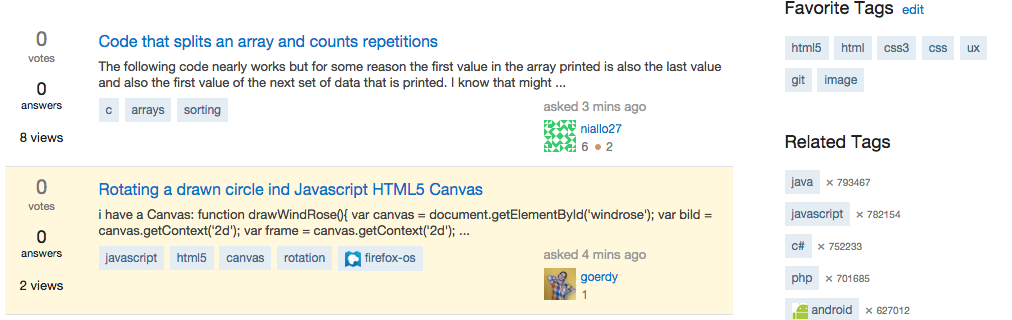
When reading a text book, an instructional book, or a cook book, its back will usually contain an index of keywords and the page numbers where you can find them. Tags work in a similar manner: they allow users to easily find content based on a single word or phrase. People create tags to refind something and share a resource with others. In a website, you can navigate through your own tags or other people’s tags.
Stackoverflow uses tags:
Pagination
Pagination is used when there are too many items to show them in one page. Linear content flows —such as articles like this— should almost never be broken up into multiple pages. Where pagination comes in handy is for listings, such as e-commerce category pages, search engine results pages, article archives and photo galleries.
For example:

:visited links
Visited links are often overlooked, but they are very helpful, especially on large websites. Knowing which pages I’ve visited is helpful in cases where I don’t want to visit them again, for example when I’m at an online store and comparing TVs to buy.
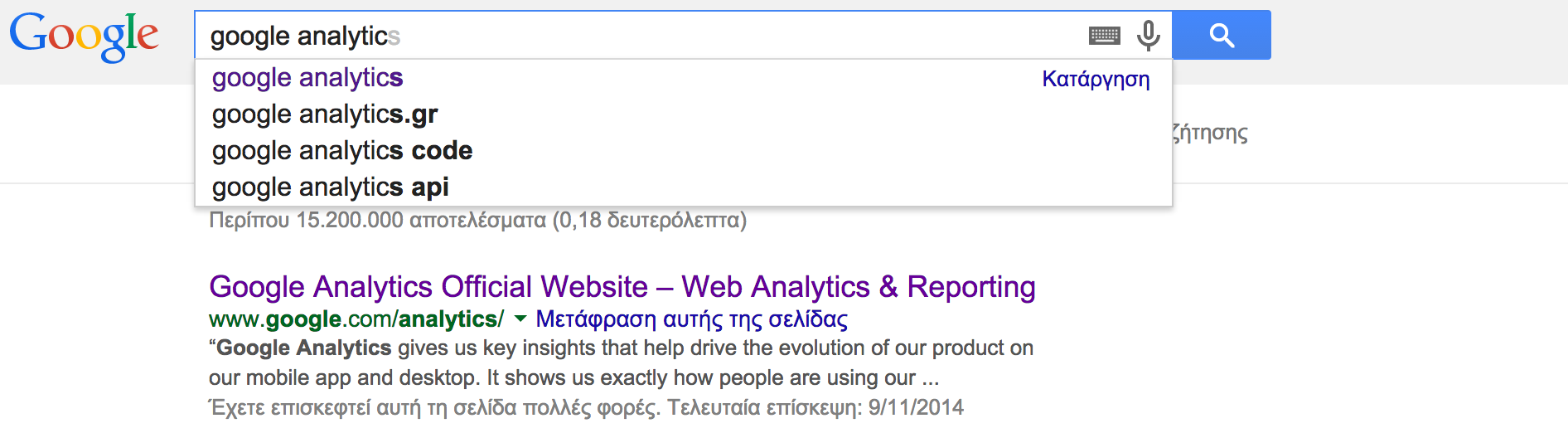
Hypertext theory and current design conventions all indicate the need to change the color of visited links. Further, empirical observations from user testing have identified several severe usability problems on sites that violate this convention.
Using different colors for visited and unvisited links makes your site easier to navigate and thus increases user satisfaction.
Google uses :visited links in its search results:
Active state of links
Note: I use the word ‘active’ as often in css we use the class name ‘.active’ for styling the menu item of the current page. I don’t mean :active state.
Letting the user know what section of the site they’re in, or what category they’re navigating through can give a huge usability boost to any site. By highlighting the link of the current page, you let your users know what link they have clicked and in which page they are. That’s why your active navigation state should always be different from the default and hover state.
Back button
“Back” button or links which lead to the previous page is another form of navigation. 49% of mobile users use their phone with one hand, which means that almost 1 out of 2 users use the “back” button a lot. Many mobile applications use gestures to navigate back and forth.
Headlines
Headlines can be used as navigation links. Even if the main page headline isn’t the same as the page title or menu active link, it describes what the page is about. On average, 8 out of 10 people will read the headline, but only 2 out of 10 will read the rest.
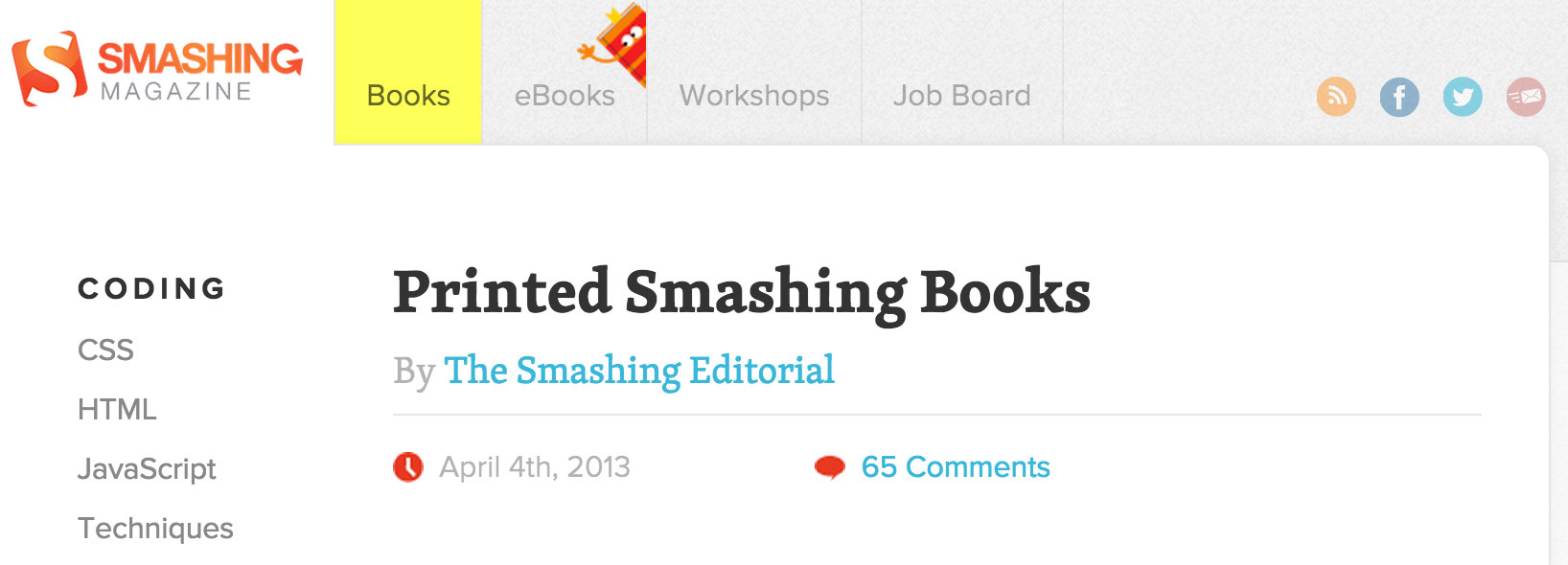
In the following example, even if I don’t see the active link on the top bar, I read the headline “Printed Smashing books” and I know that I’m in books section.
Hyperlinks
When you really think about it, the Internet is nothing more than a sea of links pointing in all different directions. Links are how people get to your site.They are a mean for the user to navigate to other pages within the same web site or view related documents and external sites. Having usable links effectively means that users are more likely to have a good navigating experience.
Users spend more time with content navigation links than they do with menus. In fact, some users don’t even look at menus. What users look at, is the page’s main content and that’s where they will usually find links that may navigate them to other pages. As users view page content, they can click on any link they find interesting. This may take them to another page of content with links they can click that lead to another page of content with more links and so forth. Before users know it, they will have consumed multiple pages of content through the clicking of different content navigation links.
Search
On a website, people usually scan for the keywords they are interested in first and only use the search function when they are unable to find a good enough navigational link. Search is usually the last resort and works when users are looking for something very specific, like a product they know the name of.
